Dr. Patil's Diabetes, Thyroid & Hormone Clinic | Dr. Himanshu Patil
Hypertension
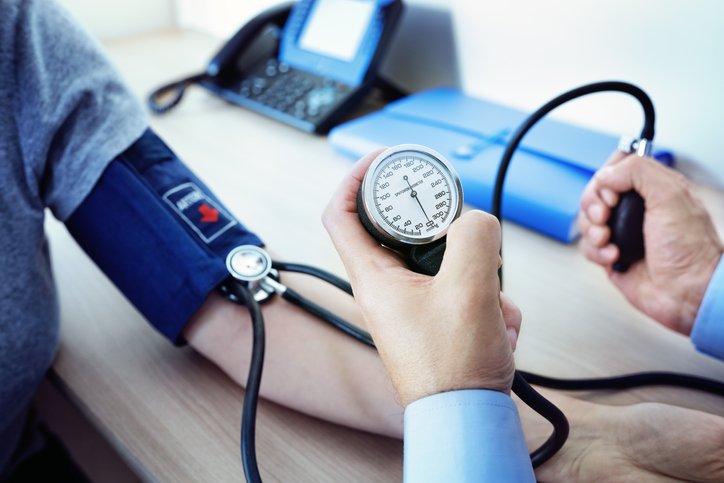
Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) is a medical condition where the force of the blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high. It is often called the “silent killer” because it typically presents no symptoms until severe damage has been done to the heart, kidneys, or other organs.
Types of Hypertension
- Primary (Essential) Hypertension:
- No identifiable cause.
- Develops gradually over years.
- Secondary Hypertension:
- Caused by underlying conditions like kidney disease, hormonal disorders, or certain medications.
Symptoms of Hypertension
Hypertension is often called a “silent killer” because it usually has no noticeable symptoms. However, in severe cases, it may present with:
- Severe headache
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Blurred vision
- Nosebleeds
- Fatigue or confusion
Causes of Hypertension
Primary (Essential) Hypertension:
- No clear cause, but linked to:
- Genetics
- Aging
- Lifestyle factors (diet, lack of exercise, stress)
2. Secondary Hypertension:
- Caused by underlying conditions, such as:
- Kidney Disorders: Chronic kidney disease, glomerulonephritis
- Hormonal Disorders: Hyperthyroidism, Cushing’s syndrome, pheochromocytoma
- Medications: Birth control pills, decongestants, pain relievers
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Interrupted breathing during sleep
- Artery Issues: Narrowing of arteries (e.g., aortic coarctation)
- Substance Use: Excessive alcohol or illicit drugs
Tretament of Hypertension
-
Lifestyle Changes:
- Diet: Low-sodium (<1,500–2,300 mg/day), DASH diet, avoid saturated fats.
- Exercise: 30 min/day of aerobic activity + strength training 2-3 times/week.
- Weight: Maintain BMI 18.5–24.9; losing 5–10% body weight helps.
- Alcohol: Quit Immediately.
- Quit Smoking & Stress Management: Yoga, meditation, deep breathing.
-
Medications:
- Diuretics: E.g., Hydrochlorothiazide.
- ACE Inhibitors: E.g., Lisinopril.
- ARBs: E.g., Losartan.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: E.g., Amlodipine.
- Beta-Blockers: E.g., Metoprolol.
- Others: Alpha-blockers, renin inhibitors, vasodilators.
-
Monitoring: Regular BP checks at home and with your doctor.
-
Secondary Hypertension: Treat the underlying cause (e.g., kidney disease).
-
Advanced Options: Device-based therapy (e.g., renal denervation) or surgery for rare cases.
Target BP:
- General: <140/90 mmHg
- Elderly/High-Risk: <130/80 mmHg
